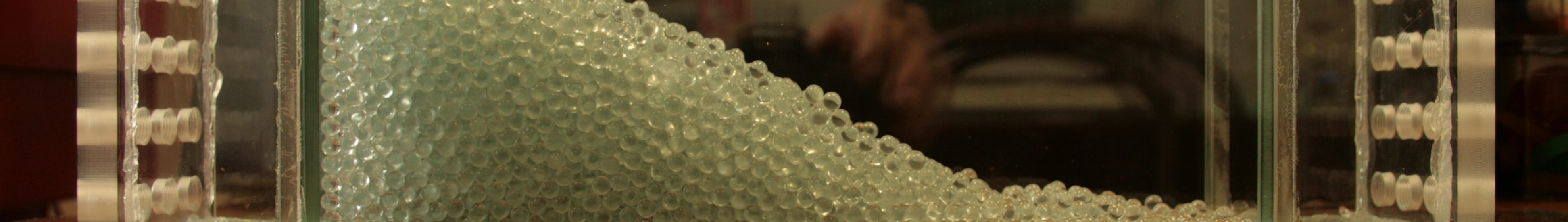
Meso-scale chute / channel / box for physical modelling of geotechnical problems
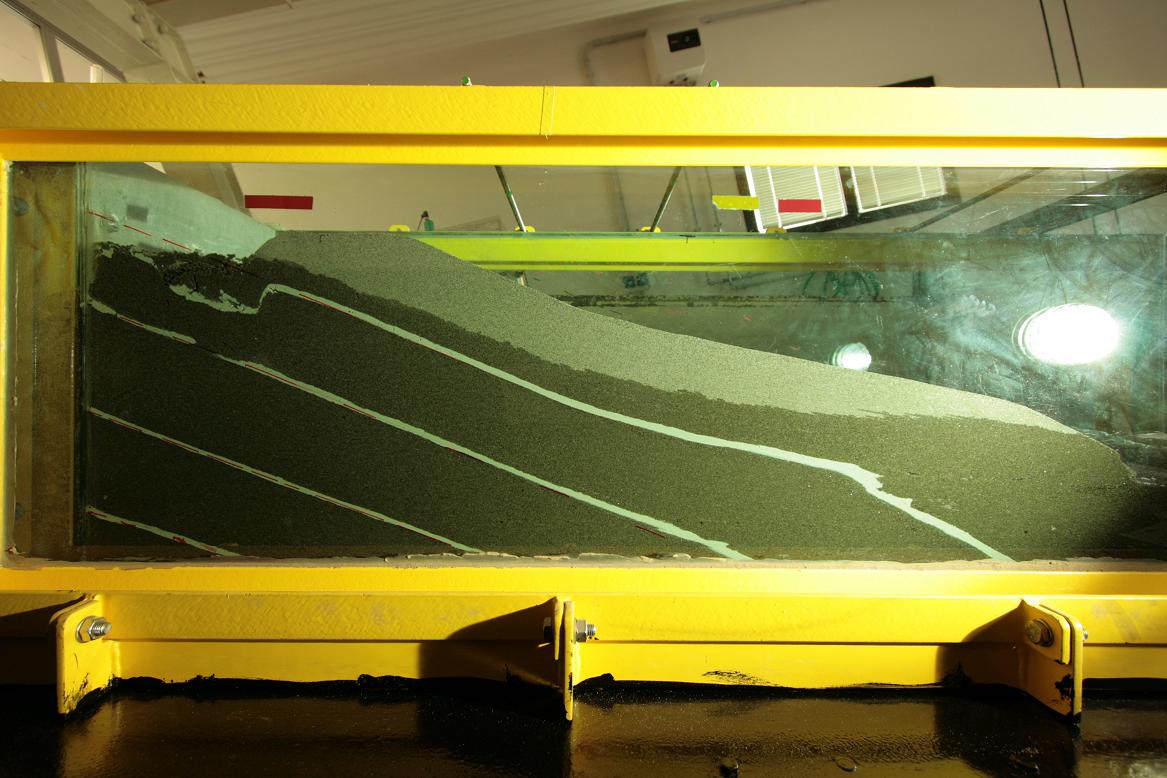
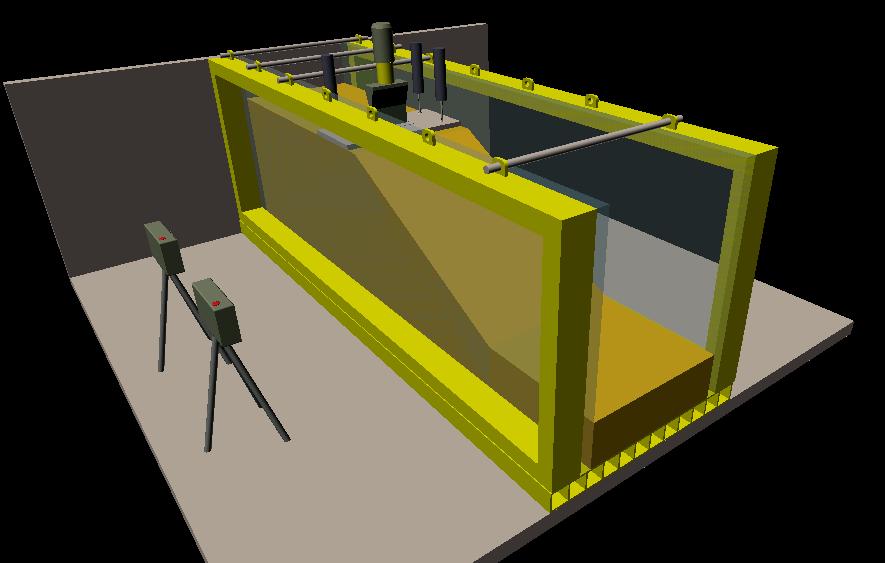


The box is equipped with a
- motorized hopper for the soil deposition by pluviation
- hydraulic jack for controlling the box inclination
- motorized loading system apparatus
- hydraulic circuit for seepage modelling and water recirculation
- photographic monitoring system
- load cells, displacement transducers, strain gauges and micro-pore water pressure transducers
High-resolution Micro-CT scanner
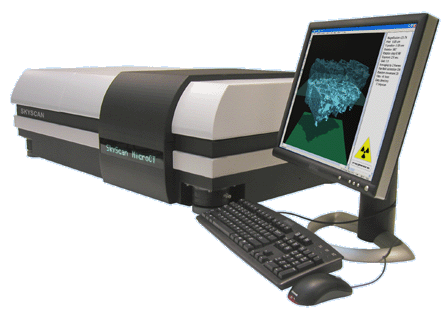

The device has the following characteristics:
- X-ray source: 20-100kV,10W,<5µm spot size or 20-80kV, 8W, <8µm spot size
- X-ray detector: 11Mp, 12-bit cooled CCD fiber-optically coupled to scintillator;
- Maximum object size: 27mm in diameter (single scan) or 50mm in diameter (offset scan);
- Detail detectability <0.8µm at highest resolution.
Schneebeli apparatus

High-speed digital cameras


DSLR cameras

(10.1 MP, max res. 3888×2592).

(18 MP, max res. 5184×3456).

(18MP APS-C, max res. 5184 x 3456).
Depth camera

Drones
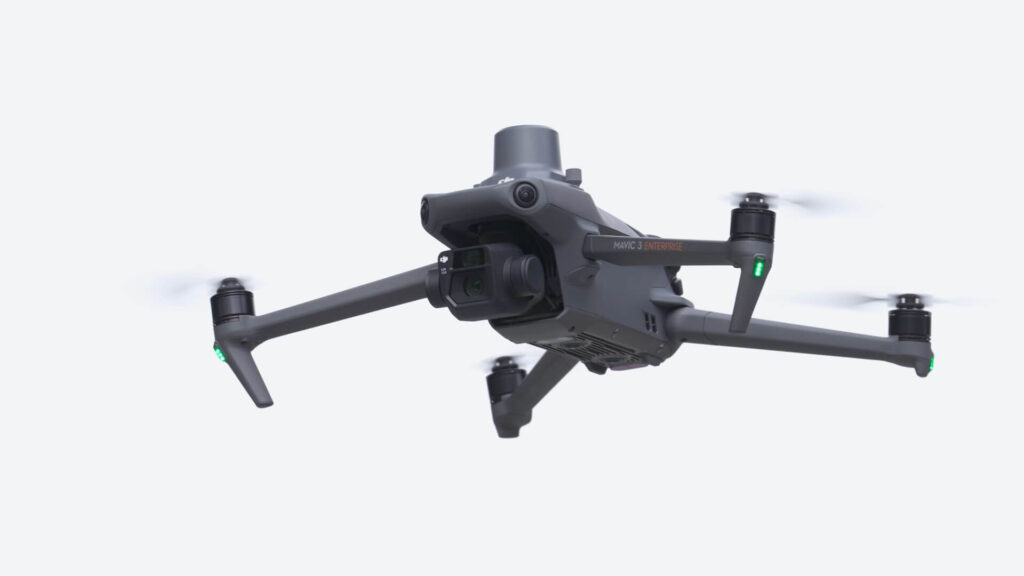

Weight: 915 g; Wide-angle camera (sensor 4/3 CMOS, 20 MP; max resolution: 5280×3956; Shutter: Electronic (8-1/8000 s) and Mechanical (8-1/2000 s); ISO Range: 100-6400 ); Telephoto Lens (Sensor: 1/2″ CMOS, 12 MP, Digital Zoom: 8x (hybrid 56x))

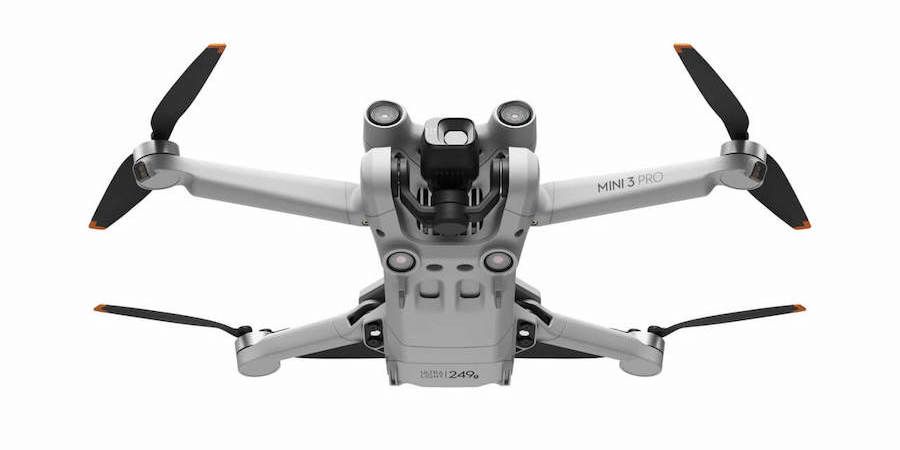
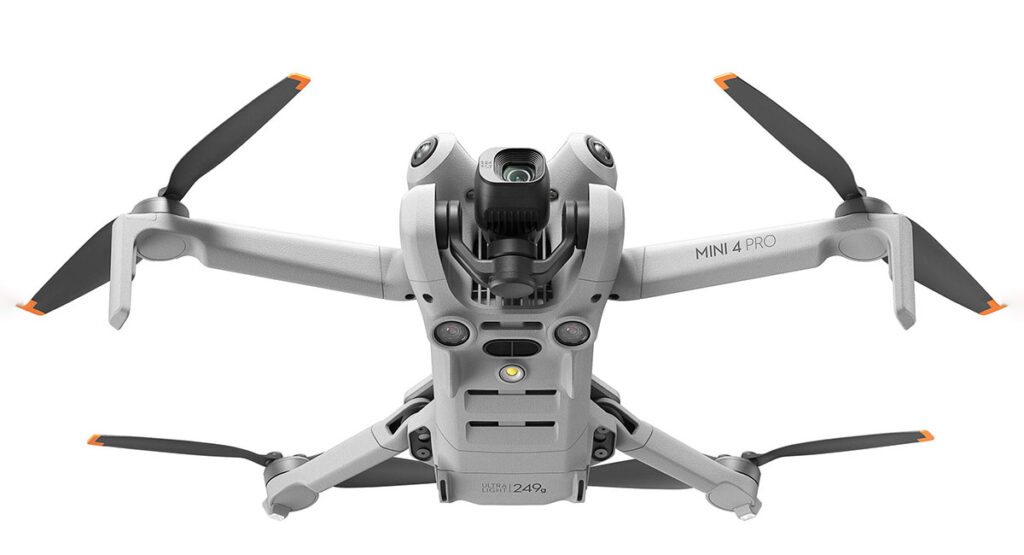
Weight: 920 g; Wide-angle camera (Sensor 1/2” CMOS , 48 MP; max resolution: 8000×6000, Shutter: Electronic only (8-1/8000 s), ISO Range: 100-25600); Telephoto Lens (Sensor: 1/2″ CMOS, 12 MP, Digital Zoom: 8x (hybrid 56x)); Thermal camera (Resolution: 640×512, Digital Zoom: 28x)


GNSS receivers

IMU-based tilt compensation; constellations: GPS/QZSS L1C/A, L2C
GLONASS L1OF, L2OF
BeiDou B1I, B2I
Galileo E1-B/C, E5b;
Positioning Accuracy:
Static: Horizontal: 4 mm + 0.5 ppm; Vertical: 8 mm + 1 ppm PPK: Horizontal: 5 mm + 0.5 ppm; Vertical: 10 mm + 1 ppm RTK: Horizontal: 7 mm + 1 ppm; Vertical: 14 mm + 1 ppm Tilt Compensation: RTK + 2 mm + 0.3 mm/°
Fiber-Optic Sensing Systems
Brillouin Optical Frequency Domain Analysis (BOFDA) and Reflectometry (BOFDR)
Spatial Resolution: Up to 20 cm
Spatial Sampling: 5 cm
Measurement Range: Up to 80 km fiber length
Measurement Repeatability: < 2 με for strain, < 0.1°C for temperature
Measurement Configurations: Supports both looped and single-ended measurements
Long-Range Option: Looped measurements up to 50 km
Ultra-Long-Range Option: Looped measurements up to 80 km with 2.5 m spatial resolution
High-Resolution Option: Spatial resolution enhanced to 20 cm for fiber lengths up to 2 km
Single-Ended Measurements: Using patented BOFDR technology
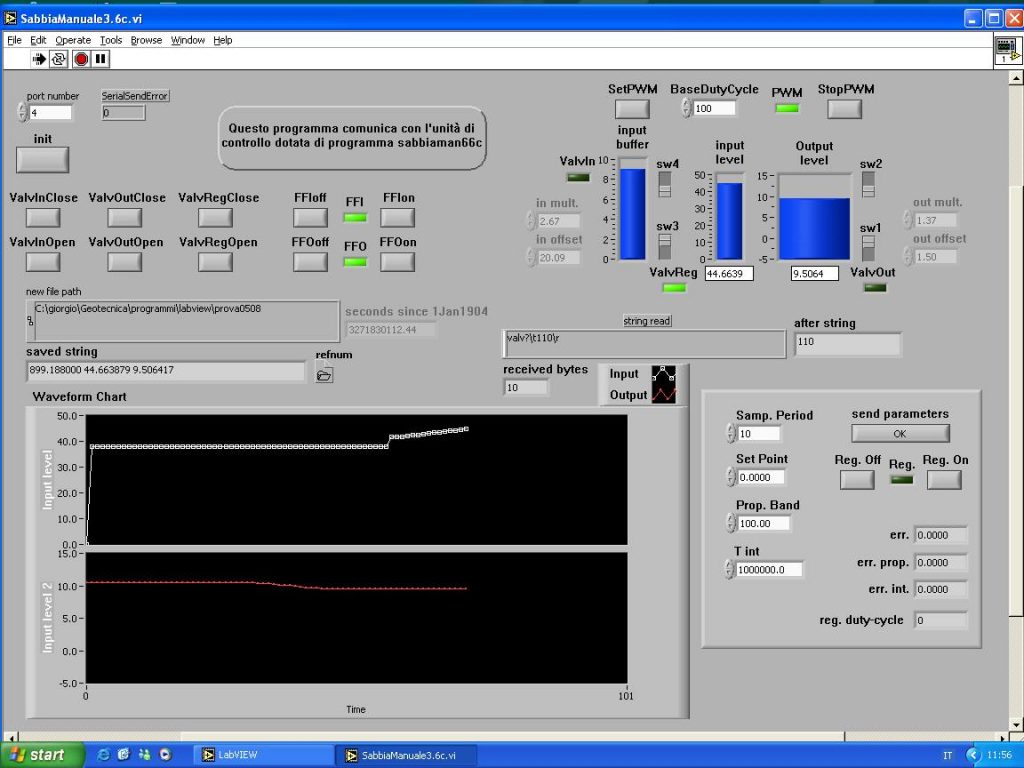
Labview
Chassis and modules




Arduino

Raspberry




Equipment

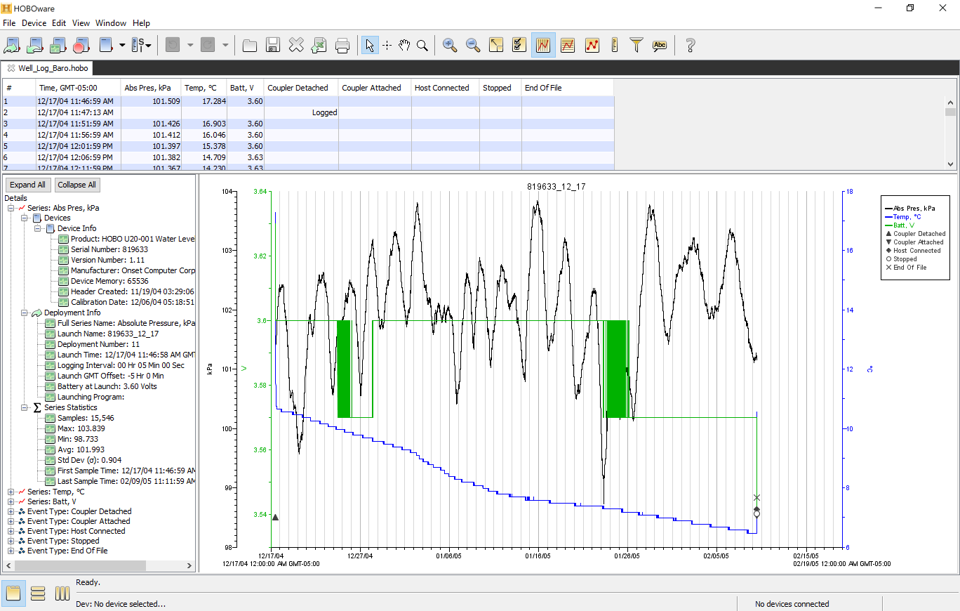
Sensors




For a glossary in the field of force measurement have a look here
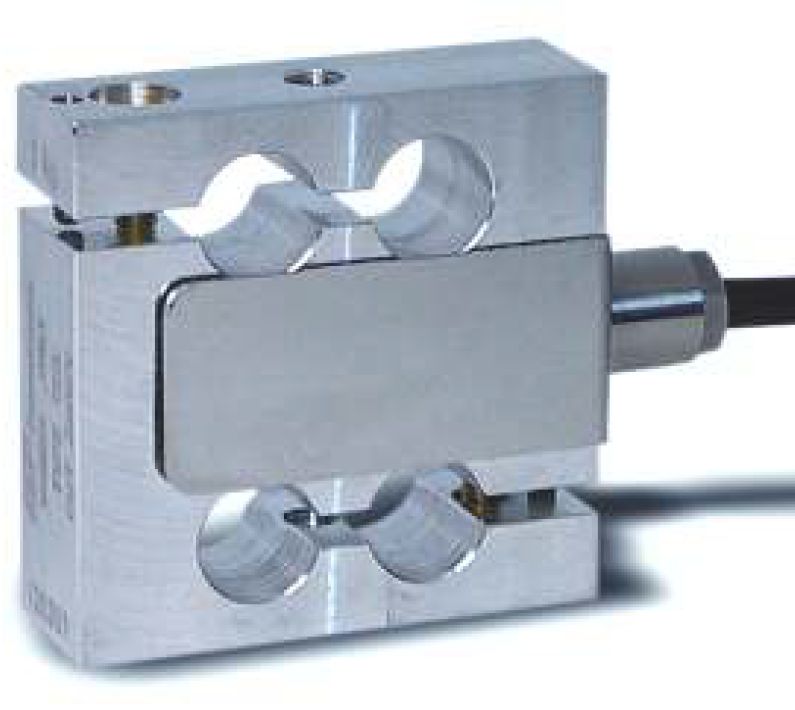


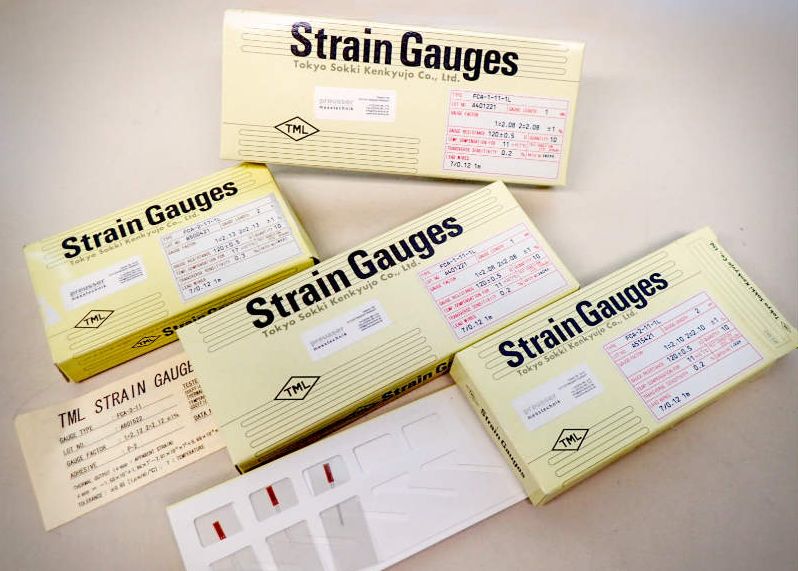
Gauge types: FLK-6-23 (gauge factor 2.15), FLK-6-17 (gauge factor 2.13)

SlimLine, Fy = -1.7 … 1.7 kN

SlimLine, Fz = 0 … 26 kN


Important video instructions on the functioning and the use of 1-component Piezoelectric force sensors:




Granular materials

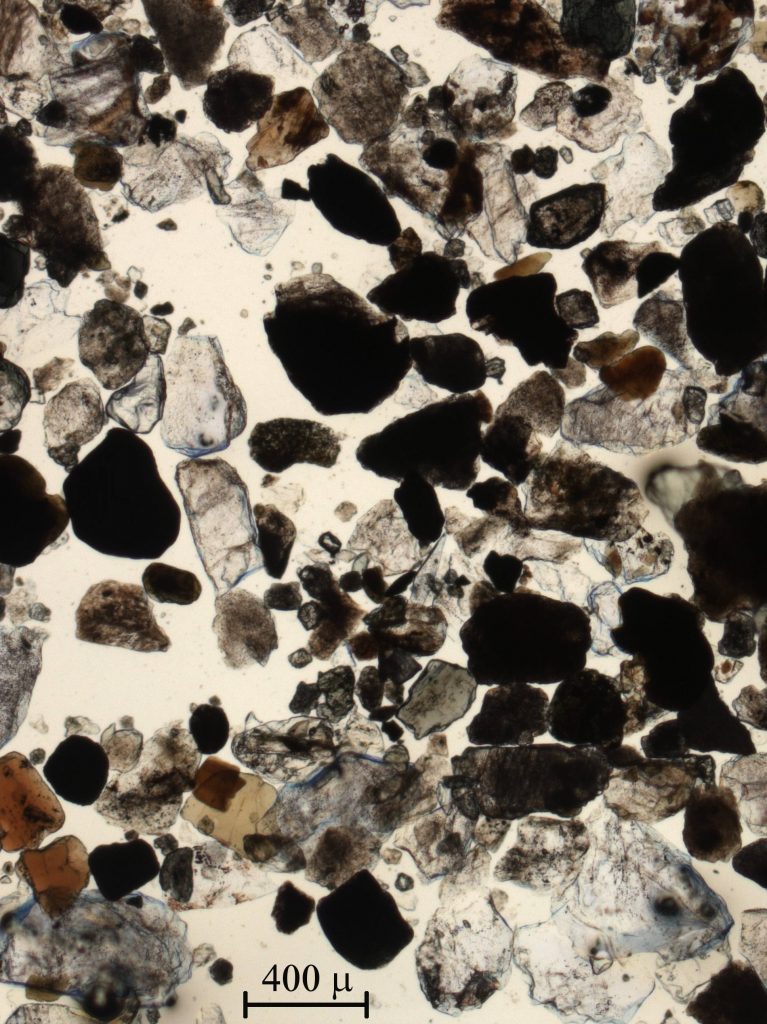

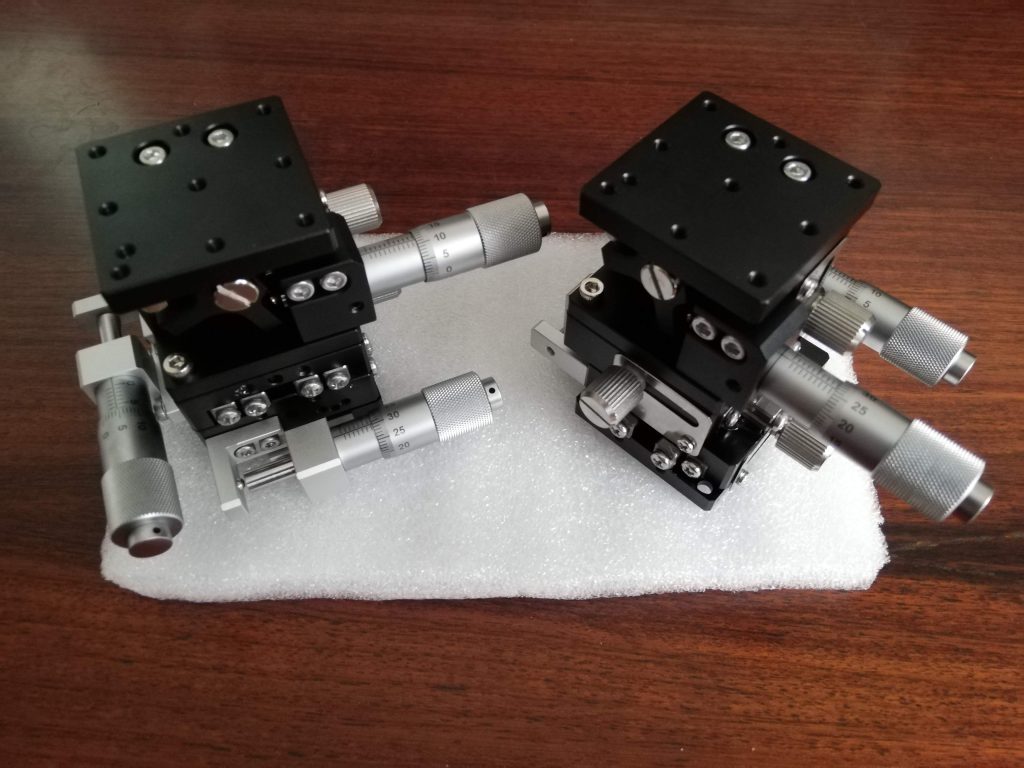
Micro-stages

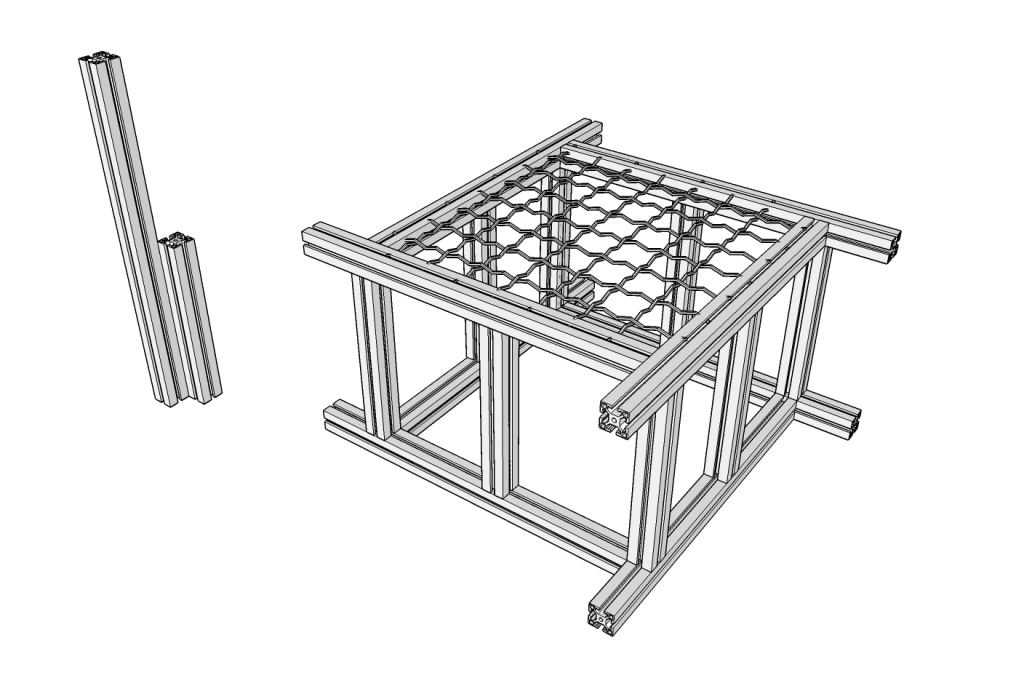
Alluminium extruded profiles

References
{5488896:EBSECQKZ};{5488896:BC4LXZ8L};{5488896:DQGI5789};{5488896:EBSECQKZ};{5488896:DQGI5789};{5488896:DQGI5789};{5488896:BC4LXZ8L}
apa
date
0
7